AudioRecorder
AudioRecorder is a primary interface for capturing audio. It supports three main modes of operations:
- File recording: Writing audio data directly to the filesystem.
- Data callback: Emitting raw audio buffers, that can be used in either further processing or streamed.
- Graph processing: Connect the recorder with either
AudioContextorOfflineAudioContextfor further more advanced and/or realtime processing
Configuration
To access microphone you need to make sure your app has required permission configuration - check getting started permission section for more information.
Additionally to be able to record audio while application is in the background, you need to enable background mode on iOS and configure foreground service on android.
- Expo
- iOS
- Android
In an Expo application you can do so through react-native-audio-api expo plugin, e.g.
{
"plugins": [
[
"react-native-audio-api",
{
"iosBackgroundMode": true,
"iosMicrophonePermission": "[YOUR_APP_NAME] requires access to the microphone to record audio.",
"androidPermissions" : [
"android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO",
"android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE",
"android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MICROPHONE",
],
"androidForegroundService": true,
"androidFSTypes": ["microphone"]
}
]
]
}
For more configuration options, check out the Expo plugin section.
For bare react-native applications, background mode is configurable through Signing & Capabilities section of your app target config using XCode
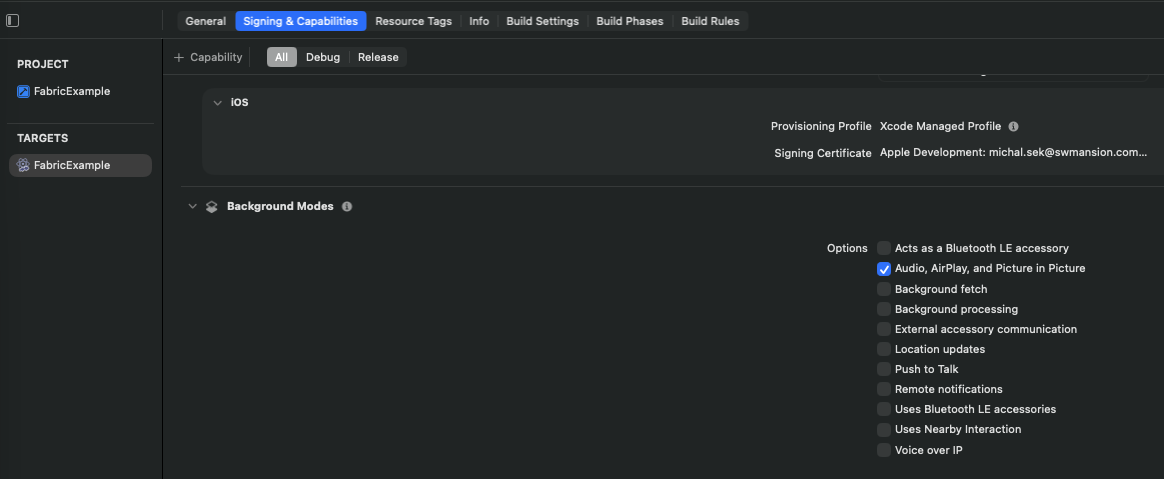
Microphone permission can be created or modified through the Info.plist file
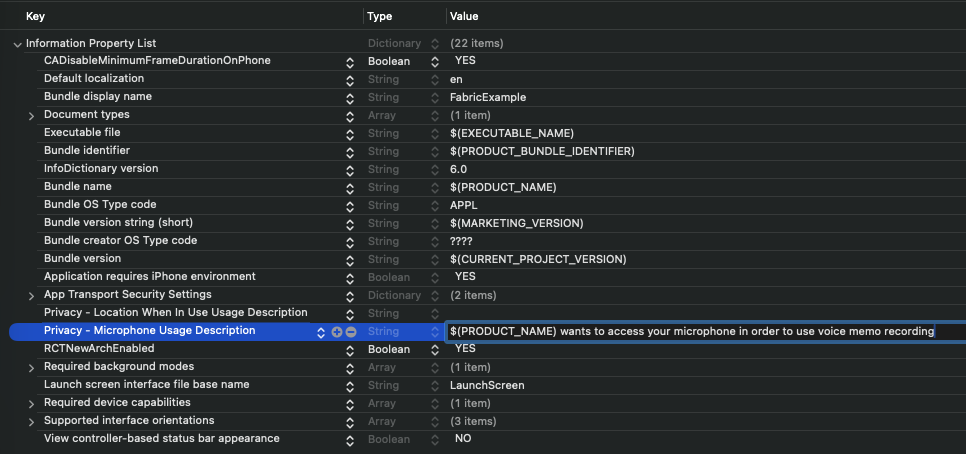
Alternatively you can modify the Info.plist file directly in your editor of choice by adding those lines:
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_NAME) wants to access your microphone in order to use voice memo recording</string>
<key>UIBackgroundModes</key>
<array>
<string>audio</string>
</array>
To enable required permissions or foreground service you have to manually edit the AndroidManifest.xml file
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<!-- Foreground service and microphone permissions for background usage -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MICROPHONE"/>
<!-- General permission for microphone access -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO"/>
<!-- Paste this inside <application> tag -->
<service android:stopWithTask="true" android:name="com.swmansion.audioapi.system.CentralizedForegroundService" android:foregroundServiceType="microphone" />
</manifest>
Usage
- Record to File
- Data callback
- Graph processing
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { View, Pressable, Text } from 'react-native';
import { AudioRecorder, AudioManager } from 'react-native-audio-api';
AudioManager.setAudioSessionOptions({
iosCategory: 'record',
iosMode: 'default',
iosOptions: [],
});
const audioRecorder = new AudioRecorder();
// Enables recording to file with default configuration
audioRecorder.enableFileOutput();
const MyRecorder: React.FC = () => {
const [isRecording, setIsRecording] = useState(false);
const onStart = async () => {
if (isRecording) {
return;
}
// Make sure the permissions are granted
const permissions = await AudioManager.requestRecordingPermissions();
if (permissions !== 'Granted') {
console.warn('Permissions are not granted');
return;
}
// Activate audio session
const success = await AudioManager.setAudioSessionActivity(true);
if (!success) {
console.warn('Could not activate the audio session');
return;
}
const result = audioRecorder.start();
if (result.status === 'error') {
console.warn(result.message);
return;
}
console.log('Recording started to file:', result.path);
setIsRecording(true);
};
const onStop = () => {
if (!isRecording) {
return;
}
const result = audioRecorder.stop();
console.log(result);
setIsRecording(false);
AudioManager.setAudioSessionActivity(false);
};
return (
<View>
<Pressable onPress={isRecording ? onStop : onStart}>
<Text>{isRecording ? 'Stop' : 'Record'}</Text>
</Pressable>
</View>
);
};
export default MyRecorder;
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { View, Pressable, Text } from 'react-native';
import { AudioRecorder, AudioManager } from 'react-native-audio-api';
AudioManager.setAudioSessionOptions({
iosCategory: 'record',
iosMode: 'default',
iosOptions: [],
});
const audioRecorder = new AudioRecorder();
const sampleRate = 16000;
const MyRecorder: React.FC = () => {
const [isRecording, setIsRecording] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
audioRecorder.onAudioReady(
{
sampleRate,
bufferLength: sampleRate * 0.1, // 0.1s of audio each batch
channelCount: 1,
},
({ buffer, numFrames, when }) => {
// do something with the data, i.e. stream it
}
);
return () => {
audioRecorder.clearOnAudioReady();
};
}, []);
const onStart = async () => {
if (isRecording) {
return;
}
// Make sure the permissions are granted
const permissions = await AudioManager.requestRecordingPermissions();
if (permissions !== 'Granted') {
console.warn('Permissions are not granted');
return;
}
// Activate audio session
const success = await AudioManager.setAudioSessionActivity(true);
if (!success) {
console.warn('Could not activate the audio session');
return;
}
const result = audioRecorder.start();
if (result.status === 'error') {
console.warn(result.message);
return;
}
setIsRecording(true);
};
const onStop = () => {
if (!isRecording) {
return;
}
audioRecorder.stop();
setIsRecording(false);
AudioManager.setAudioSessionActivity(false);
};
return (
<View>
<Pressable onPress={isRecording ? onStop : onStart}>
<Text>{isRecording ? 'Stop' : 'Record'}</Text>
</Pressable>
</View>
);
};
export default MyRecorder;
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { View, Pressable, Text } from 'react-native';
import {
AudioRecorder,
AudioContext,
AudioManager,
} from 'react-native-audio-api';
AudioManager.setAudioSessionOptions({
iosCategory: 'playAndRecord',
iosMode: 'default',
iosOptions: [],
});
const audioRecorder = new AudioRecorder();
const audioContext = new AudioContext();
const MyRecorder: React.FC = () => {
const [isRecording, setIsRecording] = useState(false);
const onStart = async () => {
if (isRecording) {
return;
}
// Make sure the permissions are granted
const permissions = await AudioManager.requestRecordingPermissions();
if (permissions !== 'Granted') {
console.warn('Permissions are not granted');
return;
}
// Activate audio session
const success = await AudioManager.setAudioSessionActivity(true);
if (!success) {
console.warn('Could not activate the audio session');
return;
}
const adapter = audioContext.createRecorderAdapter();
adapter.connect(audioContext.destination);
audioRecorder.connect(adapter);
if (audioContext.state === 'suspended') {
await audioContext.resume();
}
const result = audioRecorder.start();
if (result.status === 'error') {
console.warn(result.message);
return;
}
setIsRecording(true);
};
const onStop = () => {
if (!isRecording) {
return;
}
audioRecorder.stop();
audioContext.suspend();
setIsRecording(false);
AudioManager.setAudioSessionActivity(false);
};
return (
<View>
<Pressable onPress={isRecording ? onStop : onStart}>
<Text>{isRecording ? 'Stop' : 'Record'}</Text>
</Pressable>
</View>
);
};
export default MyRecorder;
API
Method | Description |
Constructor | Creates new instance of AudioRecorder. It is preferred to create only a single instance of the AudioRecorder class for the best performance, memory and battery consumption reasons. While the idle recorder has minimal impact on anything mentioned, switching between separate recorder instances might have a noticeable impact on the device. |
start | Starts the stream from system audio input device.
You can pass optional object with |
stop | Stops the input stream and cleans up each input access method. |
pause | Pauses the recording. This is useful when recording to file is active, but you don't want to finalize the file. |
resume | Resumes the recording if it was previously paused, otherwise does nothing. |
isRecording | Returns |
isPaused | Returns |
onError | Sets an error callback for any possible internal error that might happen during file writing, callback invocation or adapter access. For details check: OnRecorderErrorEventType |
clearOnError | Removes the error callback. |
Recording to file
Method | Description |
enableFileOutput | Configures and enables the file output with defined options and stream properties. Options property allows for configuration of the output file structure and quality. By default the recorder writes to cache directory using high-quality For further information check: AudioRecorderFileOptions |
disableFileOutput | Disables the file output and finalizes the currently recorded file if the recorder is active. |
getCurrentDuration | Returns current recording duration if recording to file is enabled. |
Data callback
Method | Description |
onAudioReady | The callback is periodically invoked with audio buffers that match the preferred configuration provided in For further information check: |
clearOnAudioReady | Disables and flushes the remaining audio data through |
Graph processing
Method | Description |
connect | Connects AudioRecorder with RecorderAdapterNode instance that can be used for further audio processing. |
disconnect | Disconnects AudioRecorder from the audio graph. |
Types
AudioRecorderCallbackOptions
interface AudioRecorderCallbackOptions {
sampleRate: number;
bufferLength: number;
channelCount: number;
}
-
sampleRate- The desired sample rate (in Hz) for audio buffers delivered to the recording callback. Common values include 44100 or 48000 Hz. The actual sample rate may differ depending on hardware and system capabilities. -
bufferLength- The preferred size of each audio buffer, expressed as the number of samples per channel. Smaller buffers reduce latency but increase CPU load, while larger buffers improve efficiency at the cost of higher latency. -
channelCount- The desired number of audio channels per buffer. Typically 1 for mono or 2 for stereo recordings.
OnRecorderErrorEventType
interface OnRecorderErrorEventType {
message: string;
}
OnAudioReadyEventType
Represents the data payload received by the audio recorder callback each time a new audio buffer becomes available during recording.
interface OnAudioReadyEventType {
buffer: AudioBuffer;
numFrames: number;
when: number;
}
buffer- The audio buffer containing the recorded PCM data. This buffer includes one or more channels of floating-point samples in the range of -1.0 to 1.0.numFrames- The number of audio frames contained in this buffer. A frame represents a single sample across all channels.when- The timestamp (in seconds) indicating when this buffer was captured, relative to the start of the recording session.
File handling
AudioRecorderFileOptions
interface AudioRecorderFileOptions {
channelCount?: number;
format?: FileFormat;
preset?: FilePresetType;
directory?: FileDirectory;
subDirectory?: string;
fileNamePrefix?: string;
androidFlushIntervalMs?: number;
}
channelCount- The desired channel count in the resulting file. not all file formats supports all possible channel counts.format- The desired extension and file format of the recorder file. Check: FileFormat below.preset- The desired recorder file properties, you can use either one of built-in properties or tweak low-level parameters yourself. Check FilePresetType for more details.directory- EitherFileDirectory.CacheorFileDirectory.Document(default:FileDirectory.Cache). Determines the system directory that the file will be saved to.subDirectory- If configured it will create the recording inside requested directory (default:undefined).fileNamePrefix- Prefix of the recording files without the unique ID (default:recording).androidFlushIntervalMs- How often the recorder should force the system to write data to the device storage (default:500).- Lower values are good for crash-resilience and are more memory friendly.
- Higher values are more battery- and storage-efficient.
FileFormat
Describes desired file extension as well as codecs, containers (and muxers!) used to encode the file.
enum FileFormat {
Wav,
Caf,
M4A,
Flac,
}
FilePresetType
Describes audio format that is used during writing to file as well as encoded final file properties. You can use one of predefined presets, or fully customize the result file, but be aware that the properties aren't limited to only valid configurations, you may find property pairs that will result in error result during recording start (or when enabling the file output during active input session)!
Built-in file presets
For convenience we have provided set of most basic file configurations that should cover most of the cases (or at least we hope they will, please raise an issue if you find something lacking or misconfigured!).
Usage
import { AudioRecorder, FileFormat, FilePreset } from 'react-native-audio-api';
const audioRecorder = new AudioRecorder();
audioRecorder.enableFileOutput({
format: FileFormat.M4A,
preset: FilePreset.High,
});
Preset | Description |
Lossless | Writes audio data directly to file without encoding, preserving the maximum audio quality supported by the device. This results in large file sizes, particularly for longer recordings. Available only when using WAV or CAF file formats. |
High Quality | Uses high-fidelity audio parameters with efficient encoding to deliver near-lossless perceptual quality while producing smaller files than fully uncompressed recordings. Suitable for music and high-quality voice capture. |
Medium Quality | Uses balanced audio parameters that provide good perceptual quality while keeping file sizes moderate. Intended for everyday recording scenarios such as voice notes, podcasts, and general in-app audio, where efficiency and compatibility outweigh maximum fidelity. |
Low Quality | Uses reduced audio parameters to minimize file size and processing overhead. Designed for cases where speech intelligibility is sufficient and audio fidelity is not critical, such as quick voice notes, background recording, or diagnostic capture. |
Preset customization
In addition to the predefined presets, you may supply a custom FilePresetType to fine-tune how audio data is written and encoded. This allows you to optimize for specific use cases such as speech-only recording, reduced storage footprint, or faster encoding.
export interface FilePresetType {
bitRate: number;
sampleRate: number;
bitDepth: BitDepth;
iosQuality: IOSAudioQuality;
flacCompressionLevel: FlacCompressionLevel;
}
Property | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
bitRate | Defines the target bitrate for lossy encoders (for example AAC or M4A). Higher values generally improve perceptual quality at the cost of larger file sizes. This value may be ignored when using lossless formats.
| |||||||||||||||||||||
sampleRate | Specifies the sampling frequency used during recording. Higher sample rates capture a wider frequency range but increase processing and storage requirements. | |||||||||||||||||||||
bitDepth | Controls the PCM bit depth of the recorded audio. Higher bit depths increase dynamic range and precision, primarily affecting uncompressed or lossless output formats. | |||||||||||||||||||||
iosQuality | Maps the preset to the closest matching quality level provided by iOS native audio APIs, ensuring consistent behavior across Apple devices. | |||||||||||||||||||||
flacCompressionLevel | Determines the compression level used when encoding FLAC files. Higher levels reduce file size at the cost of increased CPU usage, without affecting audio quality. |