interpolate
interpolate lets you map a value from one range to another using linear interpolation.
Reference
import { interpolate } from 'react-native-reanimated';
function App() {
const animatedStyle = useAnimatedStyle(() => ({
opacity: interpolate(sv.value, [0, 100], [0, 1], Extrapolation.CLAMP),
}));
}


Type definitions
enum Extrapolation {
IDENTITY = 'identity',
CLAMP = 'clamp',
EXTEND = 'extend',
}
type ExtrapolationAsString = 'identity' | 'clamp' | 'extend';
export type ExtrapolationType =
| ExtrapolationConfig
| Extrapolation
| ExtrapolationAsString
| undefined;
function interpolate(
value: number,
input: readonly number[],
output: readonly number[],
extrapolate?: ExtrapolationType
): number;
Arguments
value
A number that is going to be mapped to the output range.
input
An array of numbers specifying the input range of the interpolation.
output
An array of numbers specifying the output range of the interpolation. It should have at least the same number of points as the input range.
extrapolate Optional
The extrapolate parameter determines what happens when the value goes beyond the input range. Defaults to Extrapolation.EXTEND.
Available types:
Extrapolation.EXTEND- predicts the values beyond the output range.Extrapolation.CLAMP- clamps the value to the edge of the output range.Extrapolation.IDENTITY- returns the provided value as is.
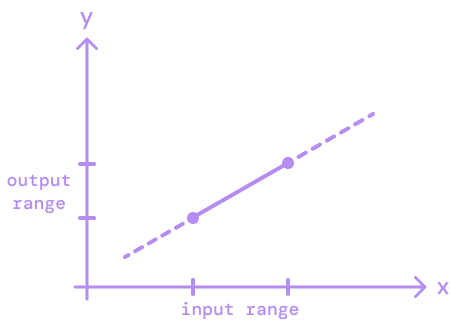
EXTEND
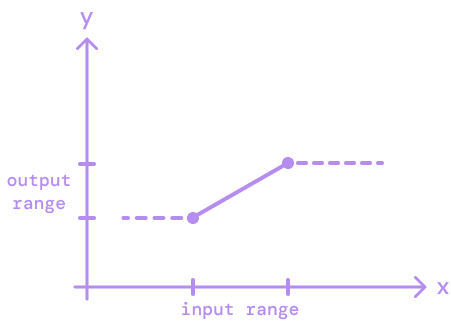
CLAMP
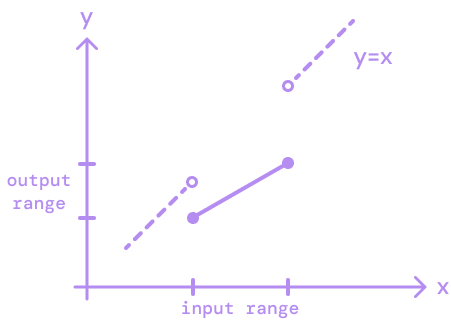
IDENTITY
This parameter also accepts string values:
"extend""clamp""identity"
By default, the extrapolate parameter applies the value passed to both edges of the range. To specify extrapolation to a particular edge, you can pass an object:
const opacity = interpolate(
sv.value,
[0, 100],
[0, 1],
{ extrapolateLeft: Extrapolation.CLAMP }
);
Returns
interpolate returns a mapped value within the output range.
Example
Platform compatibility
| Android | iOS | Web |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |